Search Results for: island
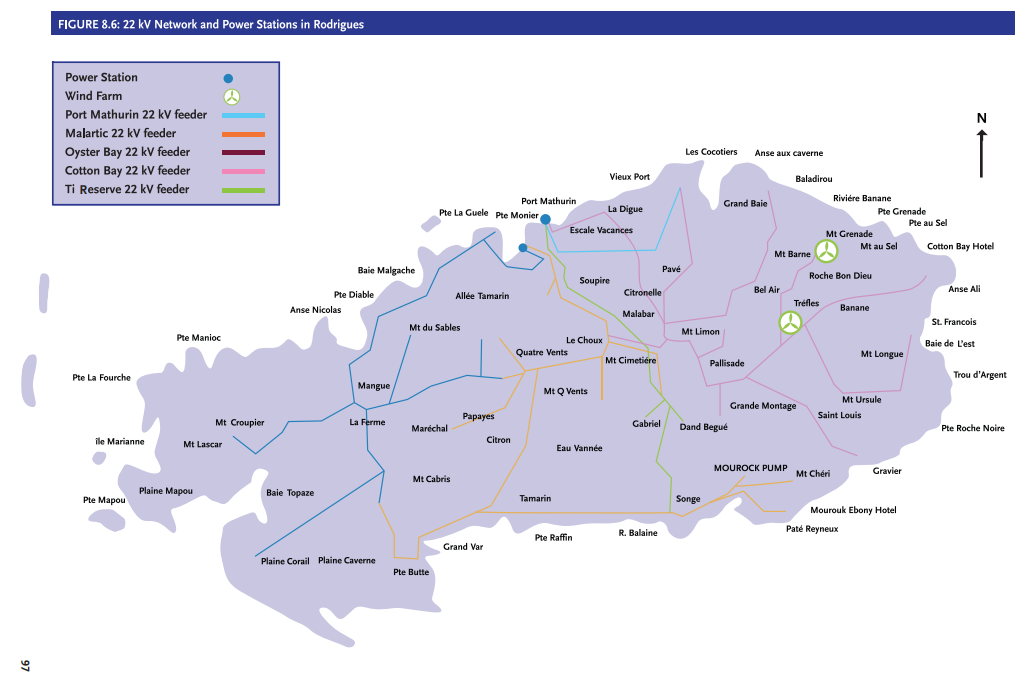
Rodrigues Island is a small volcanic island in the Indian Ocean, east of Mauritius, of which it is a territory. On the north coast, the capital Port Mathurin features colonial buildings including the former governor’s residence. In the southwest, the François Leguat Giant Tortoise and Cave Reserve is home to fruit bats and giant tortoises, plus underground caves like the stalactite-filled Grande Caverne.
There are several types of microgrids for different applications. As markets, technology, and regulation changes, the types of microgrids will continue to evolve.
Military Microgrids The ability to reliably incorporate solar PV and energy storage into military energy systems is a critical objective for the United States DOD. Reliance on diesel fuel in remote regions in the world is a weak point in military operations, and the results can be costly and deadly due to the challenge of transporting fuel through hostile regions. Additionally, the us DOD recognizes climate change as a driver of increasing instability, resulting in internal and external pressure to reduce emissions.
Campus Microgrids could refer to corporate campuses, university campuses, and military campuses. They are often CHP / Combined Heat and Power.
Community Microgrids could be considered community solar 2.0. In the developing world, community microgrids can be used to achieve electrification for the first time. In the developed world they are often used to help communities achieve renewable energy targets.
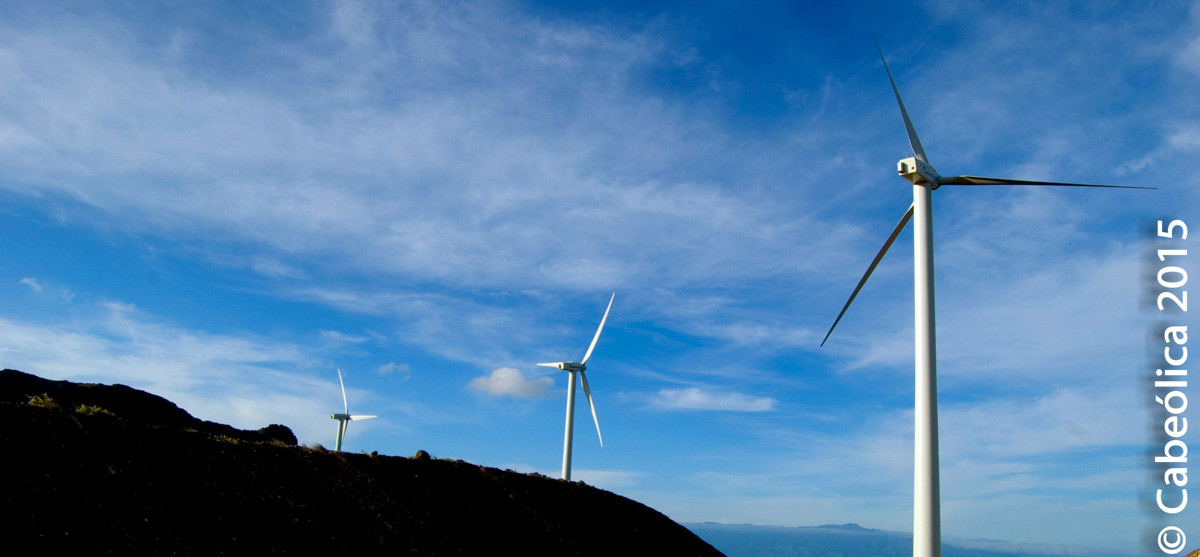
Island Microgrids are attractive due to the high cost of importing liquid fuels. While traditionally run off diesel, small and large islands around the world are incorporating renewables and energy storage into their energy systems. Examples of island microgrids.
Remote Microgrids create energy access beyond the grid. Like island microgrids, remote microgrids were traditionally dominated by diesel but are rapidly incorporating solar plus storage.
Utility Microgrids are done by incumbent electric utilities.
New Types of Microgrids:
Blockchain Microgrids allow prosumers to buy and sell electricity without electric utility involvement, and it is now becoming a reality. This democratic type of microgrid is already being deployed in New York, Africa, Europe, and Australia and electric utilities are scrambling to catch up with technology they see as a threat.
DC Microgrids An influx of DC microgrids and distribution could be inevitable as solar panels, electric vehicles, batteries, LED lights, and DC electronics flood the electric grid, prompting innovators to seek more efficient ways of stringing them all together.
Autonomous EV Microgrids are enabled by driverless electric vehicles that can fetch electricity whenever a home system or microgrid is running low. It can also get signals from wind and solar farms that they are producing too much energy, and can fill up on the cheap.
Desalination Microgrids are in demand for solving water challenges with renewables. Solar desalination can be achieved without energy storage simply by desalting during solar hours and storing the water.
Africa Microgrids
Microgrids and off-grid home solar systems in Africa are being rapidly deployed where the utility grid has failed. There are more people on the planet without electricity than when Edison first invented the lightbulb, and many of those people are in Sub-Saharan Africa. Two in every three Africans do not have access to electricity at all, instead relying on expensive and dangerous kerosene.
Given the savings over Kerosene, avoided infrastructure costs, and cascading benefits, the investment opportunity for Africa microgrids, and there is a policy push to fairly value and promote off-grid and microgrids in Saharan Africa.
MICROGRID PROJECTS IN AFRICA
The current situation presents a tremendous opportunity for microgrid developers to harness new technologies and business models to scale solutions, and many entrepreneurs have been busy doing just that.
Off the African coast is a hub for more traditional, island microgrids by companies like ABB. These microgrids are reducing their dependence on imported fuel by incorporated wind and solar generation to their existing microgrid infrastructure.
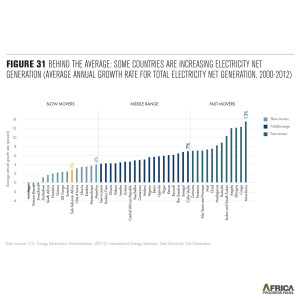
Acscension Island in Saint Helena has introduced 1650 kW of wind to its existing microgrid. Annobon Island in Equatorial Guinea boasts a 5 MW solar hybrid microgrid optimized by Princeton Power Systems. Graziosa blends solar, wind, gas turbines, NMC storage, and a Fuel Cell for its highly diversified microgrid. Robben Island, like Alcatraz in the US is a famous prison that also boasts an innovative microgrid for tourists. Graciosa in the Azores has slashed fuel imports with solar, wind, and NMC battery storage. Other African islands diversifying their microgrid mix include Santiago, Sal Island,
Africa’s mining sector have also been deploying microgrids in Africa to maintain production during frequent power outages in the middle of the continent. Electricity in the interior is often cheap thanks to hydropower and government subsidies, but reliability is low.
In South Africa, the Zwartkop Chrome Mine and and Thabazimbi Chrome Mine are operating on a gas-diesel hybrid microgrid. Also in South Africa, ABB is “drinking their own kool-aid’ with a microgrid with a large solar footprint on the ABB Longmeadow Facility.
Africa Microgrid News

Mobile Phone Adoption In Africa Can Provide Tools, Demand, and Lessons for Off-Grid Electrification
Hundreds of millions of phones (and smartphones) have been activated in Africa. But the aspiration of portable and renewable off-Grid solutions for all households still appears …

Solar Kiosk Turns a Sleepy Kenyan Village Into An Urban Center
After decades of failed initiatives to extend electricity access, over 600 million people in Africa still do not have access to electricity. With current trends, it will take …

Africa And The Policy Push For Mini-Grid Growth
In Africa’s quest for power sufficiency, there is a vehicle, a driver and the passengers. With the private sector/investor’s interest being the driver, governments & policies, …

The Investment Case for Mini-Grids and Off-Grids in Africa
Since the mid-1990s, external finance to Africa’s power sector has averaged only around US$600m per year of public assistance, plus a similar volume of private finance, according …

Microgrid Business Models Gain Traction In Kenya As Africa Leapfrogs Electric Grid
Kenya Microgrid Company SteamaCo Is Deploying Renewable Energy, Pay-As-You-Go Microgrids In Rural Africa One of the most interesting aspects of distributed energy is that rural …
With Africa’s exciting growth path and the fact that most Sub Saharan African countries are working on policies to fast track investment in the power sector & renewable energy …

Caterpillar Takes Equity Stake In Africa Microgrid Company Powerhive
Part of a $20 million round of Series A VC funding, Caterpillar Ventures is taking an equity stake in Powerhive, a pioneering developer and vendor of smart microgrids that network …

From DOD to NGO: CleanSpark Partners With Global Impact To Accelerate Sustainable Development
After completing their flagship ‘FractalGrid’ at Camp Pendleton, CleanSpark CEO Michael Firenze told Microgrid Media that 2016 would serve as the tipping point for the transition …

Microgrids in Africa: Perspectives From WorldWatch Institute and Navigant Research
This article was written by D.A. Barber for AFKInsider. It is being reposted with permission. With Africa’s push for rural electrification, microgrids — especially those that …

Renova, CleanSpark Partner to Develop Microgrid Projects Worldwide
Renova Power Networks and CleanSpark on January 5 announced a partnership to hasten development and deployment of renewable energy microgrids worldwide. Denver-based Renova has …

5 Unstoppable Drivers Of Microgrid Growth in 2016
You may not be surprised that we are bullish on microgrids, but we are unaware of an argument against significant microgrid growth in the coming years. By definition, microgrids …

Paris Climate Agreement Aftermath – How climate finance can support development and climate objectives through renewable microgrids
The Paris climate negotiations have exceeded most expectations, concluding in an ambitious global agreement on limiting carbon emissions to restrain the impacts climate change. …
India Microgrids
India has one of the most robust microgrid markets for off-grid and grid-connected systems. Microgrids in India are deployed to fill in for an unreliable utility grid, reach new off-grid customers, save money, and reduce carbon emissions. Indians who could afford it have long used diesel generators to backup the utility grid, but are increasingly moving to microgrid options consisting of solar pv, and energy storage.
India’s aggressive electric vehicle targets should also contribute to microgrid growth as homes, campuses, and companies seek to ensure adequate electric supply to meet surging demand. The car batteries themselves can play a significant role in microgrid systems, storing solar energy for when it’s needed. The Indian government is planning on offering a ‘EV as a Service’ financial model to all citizens, putting the government in a position to possibly utilize EV batteries as a grid resource to meet national renewable targets.
Microgrids in India
In Karnataka, the SELCO Foundation has deployed solar-storage remote microgrids to provide energy access in Baikampady Mangalore, Neelakantarayanagaddi Village, Mendare Village, and Kalkeri Sangeet Vidyalaya. Each of these are DC microgrids.
The Indian Coast Guard operates a microgrid in Andaman Island. Dodgy power reliability was not acceptable for the Chief Ministers Official Residence in Bihar India, which has a 125 kW solar microgrid. In the village of Dharnai, Greenpeace has gone beyond activism to solar microgrid deployment.
India Microgrid News
Renewable Mini-grids Take Root in Rural India
DC MICROGRIDS
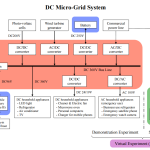
DC Microgrids are being deployed globally as distributed energy, solar PV, energy storage, consumer electronics, and LED lights are inherently DC resources. As these devices make up a large share of generation and demand, it is only natural to string them together on DC Microgrids. There are enormous opportunities for efficiency and system cost gains, as shown by research institutions, industrial facilities, and even DC homes.
DC Microgrids DC Home Solar solutions are the primary means of rural electrification for the billion people who do not yet have grid electricity. Efficient DC appliances are enabling small home solar systems and DC microgrids to handle more tasks, effectively leapfrogging the utility grid.
IEEE and several universities are addressing the issue of standards, as building codes and standards are currently written for AC distribution.
DC Microgrid News
War of Currents Unsettled as Distributed Energy, Efficient Loads, and Microgrids Go DC
List of DC Microgrid Projects
Hefei University of Technology Microgrid
–Bosch DC Microgrid at California Honda Facility
CA, North America, USConstructionBuilding, DC, Industrial
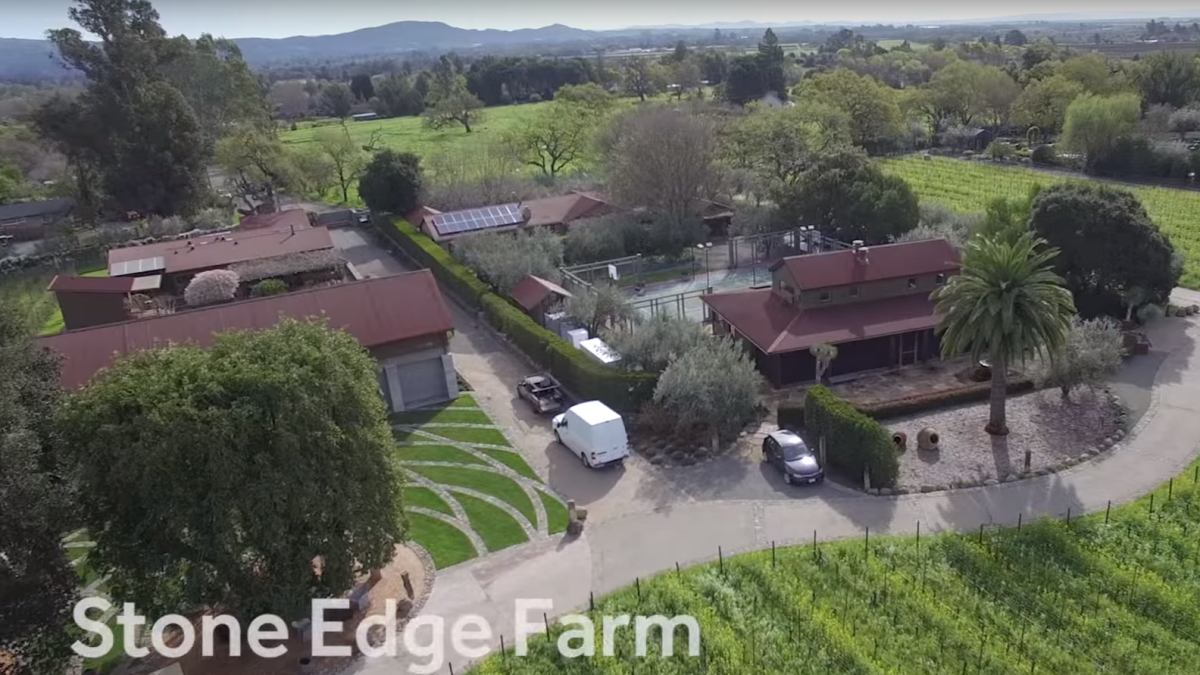
 Stone Edge Farm Winery Microgrid
Stone Edge Farm Winery Microgrid
CA, USOperationalBuilding, Commercial
Canada, North America, OntarioOperational, R&DBuilding, Industrial
 Xiamen University DC Microgrid
Xiamen University DC Microgrid
ChinaOperational, R&DUniversity
 Intelligent DC MIcrogrid Living Lab
Intelligent DC MIcrogrid Living Lab
Denmark, EuropeFeasibility, Planning, R&DBuilding, DC, University
 Coconut Island DC Microgrid (Moku o lo’e)
Coconut Island DC Microgrid (Moku o lo’e)
HI, North America, USOperationalDC, Island
–Andaman Island – Indian Coast Guard Microgrid
IndiaOperationalIsland, Military
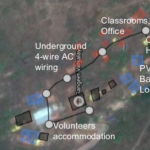 Kalkeri Sangeet Vidyalaya DC Microgrid
Kalkeri Sangeet Vidyalaya DC Microgrid
India, KarnatakaOperationalBuilding, Community, DC
North America, VAFeasibility, Operational, R&DDC, Military
State-of-the-art microgrid project sets the stage for future of energy applications
PITTSBURGH, Pennsylvania and AUSTIN, Texas – April 26, 2016 – Aquion Energy, Inc. (Aquion), developer and manufacturer of Aqueous Hybrid Ion (AHI™) batteries and energy storage systems, and Ideal Power Inc., (NASDAQ: IPWR), a developer of innovative power conversion technologies, announce today the installation of Aquion’s AHI™ batteries using Ideal Power’s Grid Resilient 30 kW Multi-port Power Conversion System as part of a state-of-the-art microgrid at Stone Edge Farm, a 16-acre organic winery and farm in Sonoma, California. The energy storage project is designed to provide a range of benefits, from integrating renewables to reducing overall energy costs, proving the broad possibilities of microgrid architectures.
The solar PV + storage installation is part of the farm’s innovative microgrid and is designed to provide energy for a number of buildings on the site, including the primary residence, offices and workshops. During daylight hours, solar PV provides energy for the buildings and charges the batteries. During nighttime hours and periods of cloud cover, the batteries provide energy for building loads.
The system consists of fourteen 25 kWh Aquion M-Line Battery Modules providing approximately 350 kWh of energy storagecapacity, connected to a 32 kW solar array using Ideal Power’s 30 kW multi-port power conversion system. The Ideal Power multi-port system architecture enables the direct DC-level connection of solar PV and energy storage in one compact, highly efficient, transformerless package, eliminating the complexities and redundancies of older, AC-coupled systems. Aquion’s safe and environmentally friendly battery technology is a unique saltwater chemistry made from abundant, nontoxic materials. The batteries are designed for daily deep cycling in long duration (4+ hour charge/discharge) applications, making them ideal for solar installations.

Aquion batteries during installation at Stone Edge Farm
The microgrid project, developed by Wooster Engineering Specialties, a general engineering contractor, provides solar self-consumption, peak shaving and load shifting services to Stone Edge Farm for energy self-sufficiency and to reduce its carbon footprint. The grid-tied microgrid is capable of islanding and operating autonomously, and is also generating sufficient energy that Stone Edge Farm is able to sell a substantial amount of the energy produced back to local utility PG&E.
“The Stone Edge Farm project is an excellent example of how long-duration advanced batteries plus solar PV can enable on-site renewable energy generation and maximize solar self-consumption. Our clean and sustainable batteries are a natural fit to help the farm meet its zero carbon emissions goal. We’re proud to be part of the Stone Edge project and their cutting-edge efforts to leverage clean energy technologies in support of their business and the planet,” said Scott Pearson, CEO of Aquion Energy.
“Microgrids utilizing renewable energy and energy storage technologies will be a crucial part of the global energy infrastructuremoving forward,” commented Dan Brdar, CEO of Ideal Power. “This project will provide an important model for the development of microgrids in the future. We’re proud that our power conversion system was selected as part of this Aquion project to help lay the foundation for new energy applications.”

Aerial view of Stone Edge Farm
Ideal Power and Aquion previously announced a technology partnership in which they tested Ideal Power’s power conversion systems alongside Aquion’s AHI™ batteries to ensure seamless interoperability and optimal performance for a range of applications. This project is the first commercial deployment of the two companies’ technologies alongside one another for an energy storage application.
The world’s first megawatt-scale renewable energy plus storage system, currently being built on the island of Graciosa in the Azores (Portugal), will set new standards for islands worldwide. Furthermore, by stabilizing the grid without the rotating mass of a conventional thermal engine, the system will enable the grid to be fully powered by wind and solar energy. The centerpiece of the system is a fully automated, intelligently managed 2.8 megawatt battery park integrated into the intelligent energy management system developed by Younicos. In addition, the system will incorporate wind (4.5 MW) and solar (1 MW) power resources, and intelligent inverters. The renewable energy-powered grid will boost the island’s annual share of renewable energies, from a previous limit of 15 percent to up to 65 percent and thus allow the island to reduce its dependence on fuel imports.